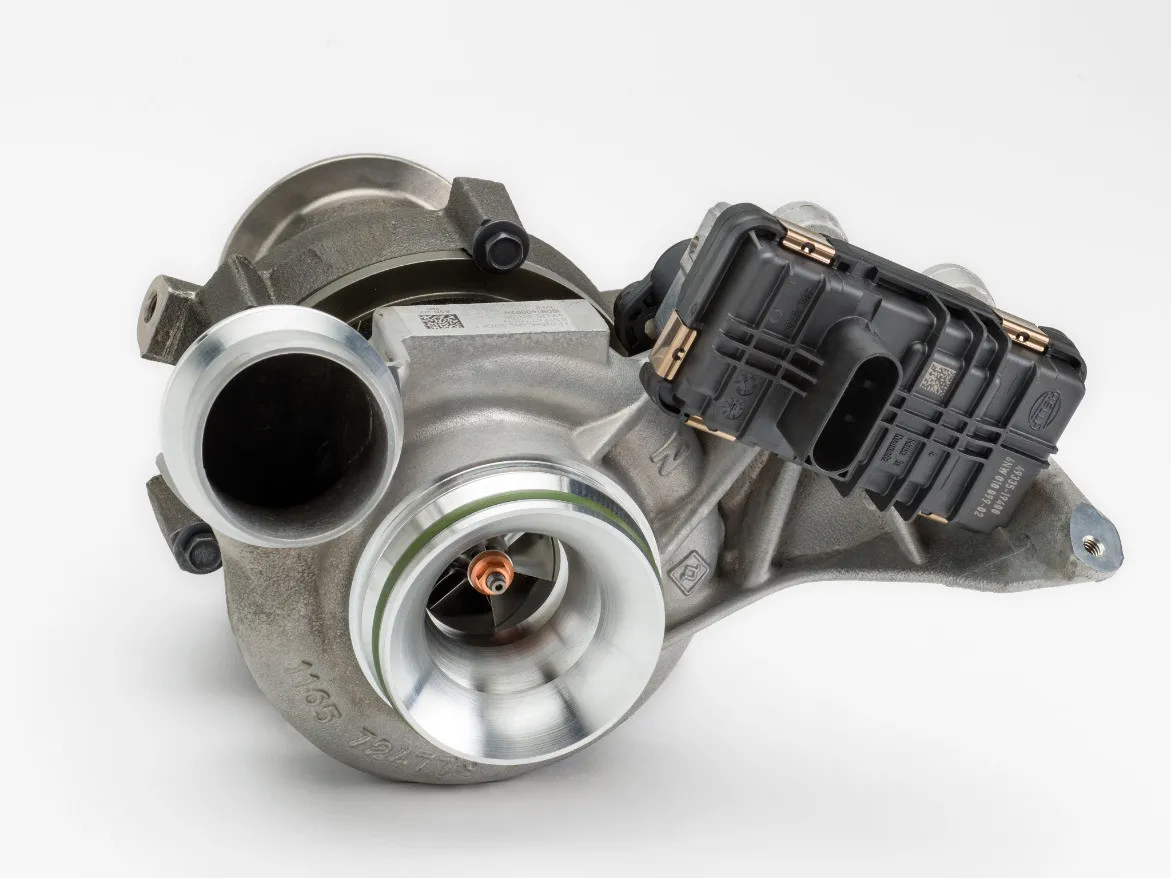
When addressing the diagnosis of a turbocharger, it is vital to be aware of the possible symptoms and understand the complex interconnection between the turbocharger and the surrounding systems.
This diagnostic process can be challenging due to the possibility of misleading symptoms, leading the technician to misinterpret the origin of the problem.
Turbocharger malfunction is often not an isolated issue but is intrinsically linked to possible failures in adjacent systems. Therefore, precise and meticulous analysis is essential to avoid incorrect diagnoses and ensure that any intervention is directed not only at correcting the turbocharger but also at the interdependent systems that can influence its performance.
Check for excess pressure in the crankcase and proper functioning of the engine breather;
Ensure that the oil used complies with all standards indicated by the manufacturer;
Check for oil or carbon buildup in the turbine;
Check oil channels and ensure there are no obstruction points;
Check hose condition and connection points;
Look for lubrication problems in the block;
Check air filter;
Check vehicle filters;
Check hose and piping condition;
Ensure proper functioning of the injection system;
Ensure the exhaust system is not obstructed.
Check connections and support or fixing points;
Look for leaks in the intercooler.
Most problems associated with the turbocharger are the result of issues external to the component. Recognizing symptoms and their causes in a timely manner can prevent more expensive repairs and reduce vehicle downtime.
Checks to Perform:Ensure that lubrication reaches the turbocharger in perfect condition, considering flow and pressure;
Replace air filter and if applicable replace the breather filter;
Check pressure, vacuum, and lubrication piping – Look for obstructed or leaking channels;
Replace gaskets of various existing connections, or if recommended use exhaust putty. Check for leaks after assembly;
Introduce oil into the turbocharger, through the lubrication inlet, in order to lubricate all internal components before the component starts operating;
Replace oil, engine oil filter and check for any type of contamination;
After starting the vehicle, let the engine idle for 3 to 4 minutes without accelerating;
Check the motor oil level.