This article provides a brief overview of the power steering system found in light commercial and passenger vehicles. The article is divided into two parts: in this section, the general function of the steering system and the importance of each of its components will be explained. In the second part of the article, the main types of power steering systems will be presented, along with the differences between them and their impact on driving comfort and safety. The main goal of power steering is to facilitate vehicle control, allowing the driver to apply less force on the steering wheel to move the wheels, resulting in a smoother and safer driving experience, regardless of road conditions.
In terms of regulations for passenger cars in the European Union, the force required to turn the steering wheel to describe a 12m radius circle from the tangent line must not exceed 200N. If the vehicle is equipped with a power steering system, in the event of auxiliary power failure, the vehicle must be able to describe a 20m radius circle, and the force should not exceed 300N.
Ensure a safe drive! Book now at LD Auto - Bosch Car Service and take care of your vehicle's steering system. Enjoy professional and efficient service.
There are various types of power steering systems. These include mechanical steering systems, rack-and-pinion systems, hydraulic power steering systems—which encompass Servotronic and electro-hydraulic power steering systems—electric power steering systems, and active steering systems, which can be combined with hydraulic power steering and electric steering systems.
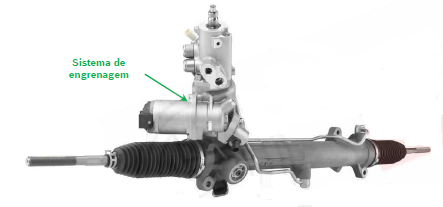
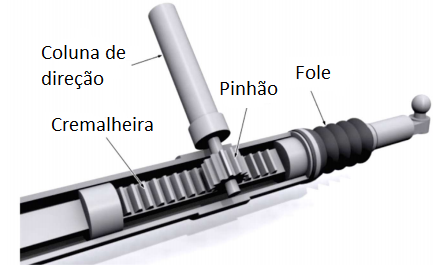
The rack and pinion steering system transforms the rotation applied by the driver into a linear movement, which is transmitted to the wheels. The rotational movement is applied, through the pinion, to the rack, making it slide and transmitting the linear movement to the steering rods, which in turn are transmitted to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to change direction.
The main advantages are:
The hydraulic steering system uses hydraulic pressure to multiply the force applied on the steering wheel to the vehicle's front wheels.
The hydraulic pressure is typically generated by a hydraulic pump driven by the combustion engine through a belt. The pressure provided by the pump supplies the "force" needed for power steering, and the steering box mechanism regulates the hydraulic fluid's power. The higher the force applied to the steering wheel, the greater the hydraulic fluid pressure, and consequently, the greater the force applied to the wheels. The most commonly used mechanism in these systems is rack and pinion.
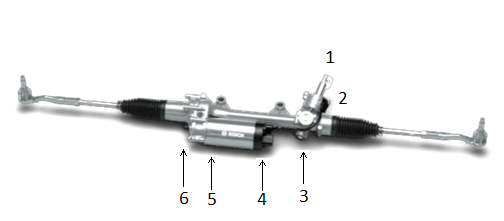
Servotronic is a rack-and-pinion steering system that varies depending on the vehicle's speed and is electronically controlled.
Using an electro-hydraulic transducer, the hydraulic return effect varies with speed, and the force required on the steering wheel increases with higher speeds, while only minimal forces are required at low speeds, such as when parking or maneuvering. This system provides a comfortable and safe driving experience.
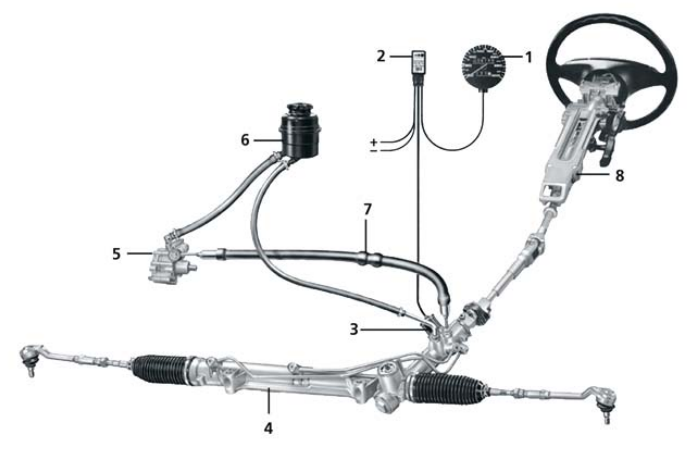

Figure 3 - Hydraulic steering system - Servotronic
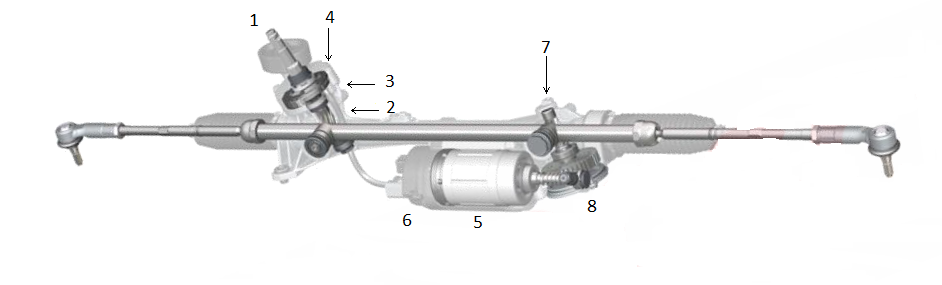
The electro-hydraulic power steering is based on the hydraulic steering system. As seen in the following image, the main difference is in the electronic activation of the pump, which generates the necessary pressure for hydraulic assistance.
The electric motor driving the pump generates the required amount of energy only when needed, saving fuel, as unlike the fully hydraulic system, it does not rely on the combustion engine to generate the pressure required for operation.

Figure 4 - Hydraulic steering system - Electro-hydraulic
In recent years, manufacturers have adopted electric power steering, eliminating hydraulic steering systems from the market. This system has several advantages, such as:
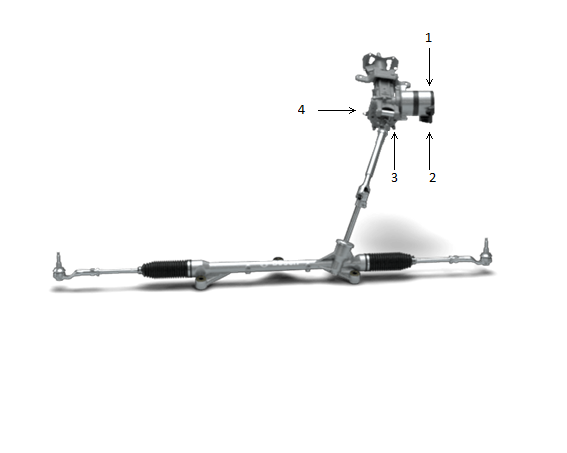
In the figure below, it is integrated into the steering column and connected to the pinion and rack steering type through a universal joint. The binary sensor is placed next to the helical gear, and based on the information about the torque generated by the electric motor, the assistance force is transmitted to the steering column through the helical gear.
This system meets the highest safety and reliability standards without compromising the driving feel and steering feedback.