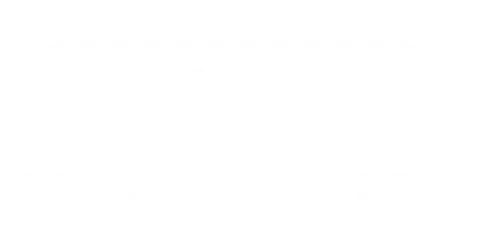Particle filters are essential components for reducing pollutant emissions in vehicles, especially in diesel engines, and are increasingly common in gasoline engines. They act as mechanical filters, capturing particles through a ceramic structure that directs exhaust gases through filtering channels.
The particle filter works as a mechanical filter and is usually made of a ceramic composite with a honeycomb-like geometry, with alternating closed and open channels, as shown in Figure 1. The particles are trapped/filtered by the walls of the channels as the exhaust gases pass through them.
Like any mechanical filter, particle filters require cleaning, known as regeneration, which can be passive, active, or a combination of both.
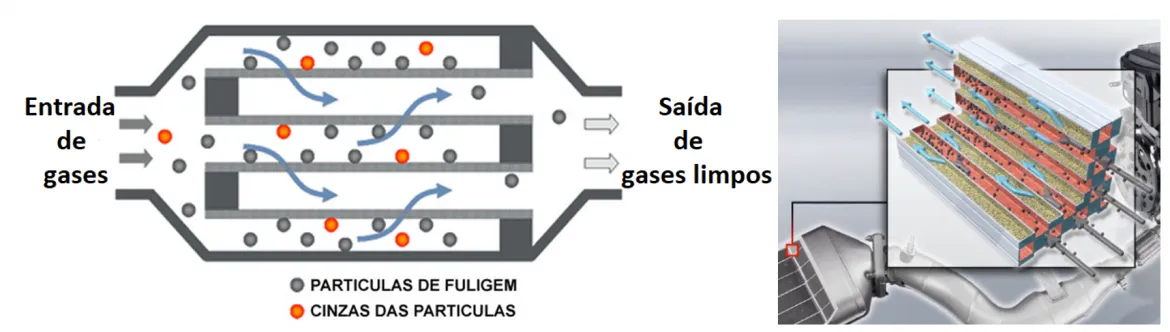
Figure 1 - Particle Filter
The particle filter is essential for reducing emissions and ensuring the engine runs smoothly. Need information on maintenance or regeneration? Our team is ready to help.
Regeneration is the essential cleaning process for the efficient operation of particle filters in combustion engine vehicles, preventing saturation and maintaining the particle capture capacity. The two main types of regeneration are passive regeneration and active regeneration, each with specific operating characteristics, temperature requirements, and conditions.
A vehicle with a passive regeneration system is less dependent on the user's driving style. This type of system requires much lower regeneration temperatures than those needed for active regeneration systems.
Typically associated with the particle filter, there is an upstream oxidation catalyst. The oxidation catalyst removes CO and HC and oxidizes NO in the exhaust gases, turning it into NO₂. When NO₂ enters the particle filter, it reacts with the particles, eliminating them, resulting in NO and CO₂.
Regeneration in these systems occurs almost continuously and becomes possible from 250 ºC.
Another solution found in some vehicles is the use of additive-enhanced passive regeneration systems. In these systems, an additive is injected along with the fuel, which, upon contact with the particles in the filter, lowers their combustion temperature. For the proper functioning of these systems, the exhaust gas temperature in the filter must be above 380ºC.
Under normal circumstances, active regeneration occurs when the filter begins to become saturated, typically when it reaches around 45% of its capacity or every 1000 km.
During active regeneration, the following changes occur in the vehicle's operation:
Depending on the condition of the filter and the presence of other diagnosed issues, the filter can either be cleaned or rebuilt.
The complexity of exhaust systems is increasing, as vehicles are now commonly equipped with specific catalysts for treating NOx, such as SCR catalysts with AdBlue injection or LNT catalysts, in addition to the oxidation catalyst and particle filter. This complexity brings with it an increase in sensors and actuators to monitor and control the exhaust system.
For this reason, LD Auto, a specialist in repairing these components, recommends that whenever a particle filter or catalyst is removed for servicing, it should be accompanied by a diagnostic report and error codes. This information is essential for a successful intervention.
The particle filter plays a crucial role in reducing emissions and protecting the engine. Want to learn more about cleaning, maintenance, or regeneration? Contact our specialized team!
The pulsed cleaning method is generally performed without opening the component, using water or specific cleaning products. If cleaning products are used, their selection is very important, as some products can damage the functioning of the catalysts, causing them to lose their chemical properties.
These services are performed by injecting air or water (more common) through the filter's entry flange. The cleaning tends to be unidirectional, cleaning the filter in only one direction. Below, in Figure 2, a schematic representation of a component composed of a catalyst and particle filter is shown.
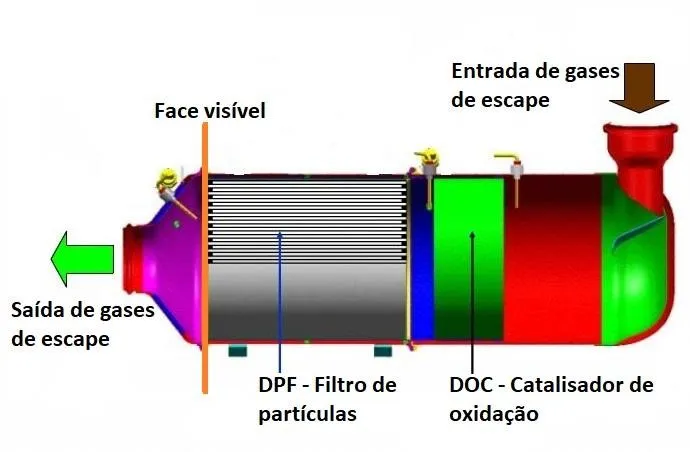
Figure 2 - Schematic representation of component (DOC + DPF)
It is easy to see that without opening the component, the inner faces of the catalyst and particle filter cannot be analyzed due to lack of access, which reduces the reliability of the repair. By analyzing Figure 2, it is clear that without opening the component, the operator will only be able to check the state of the filter's exit face (identified in orange), and the state of the other areas will remain unknown.
The soot, when in contact with cleaning products, forms mud, which, depending on the condition of the component, can be difficult to clean.
In bidirectional cleaning (Figure 3), the component is opened to expose the faces of the particle filter and catalysts, and the cleaning is done in both directions, without the use of chemicals.
Opening the component allows for excellent access and analysis of the ceramic material. This sometimes allows for small damages or defects to be corrected without the need to replace the entire ceramic material (if damaged). No chemicals are used in this cleaning process, and each cell is cleaned individually in both directions.
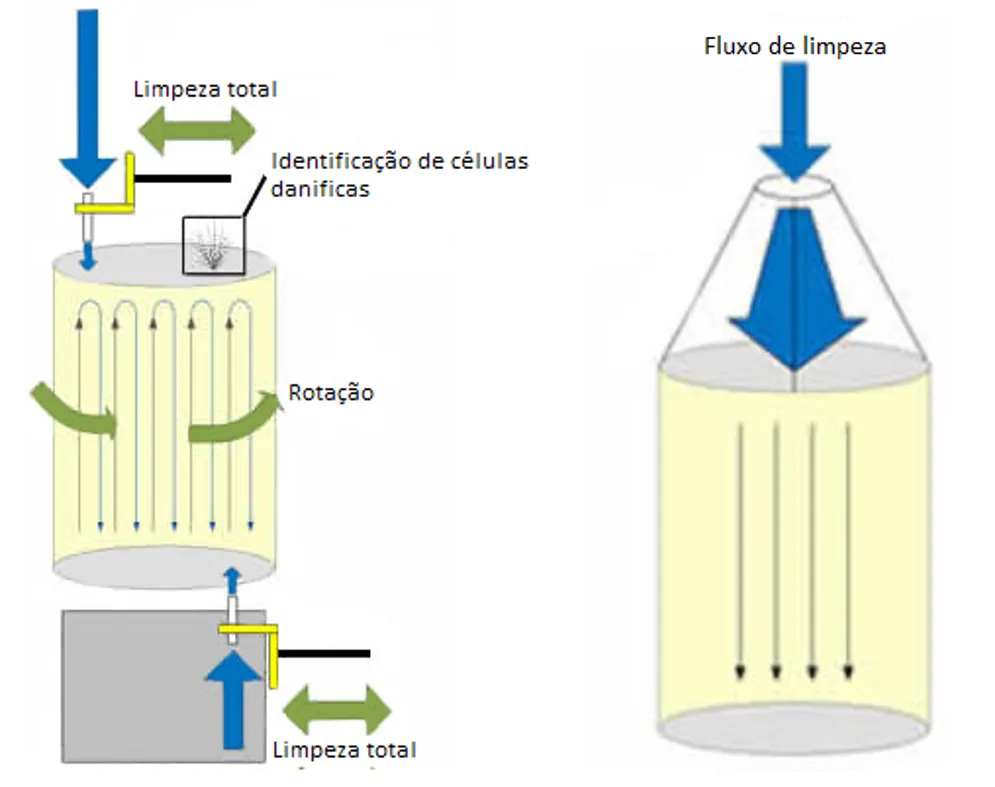
Figure 3 - Bidirectional cleaning vs pulsed cleaning
This method takes more time; however, it is a reliable process that yields good results while maintaining a competitive price. Additionally, because no chemicals are used, it is safer for both the properties of the catalysts and the environment.
When cleaning is not possible due to damage to the component or chemical inefficiency of the catalysts, it is possible to reconstruct the components (catalysts and/or particle filter), replacing the ceramic material with new material, using the original exterior.
The table below presents a summary of the main characteristics of each cleaning method:
| Parameter | Bidirectional Cleaning w/ Opening | Pulsed Cleaning w/o Opening |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning | - Cleaning executed from both sides, cell by cell. | - Mainly central zone, due to the concentration of cleaning fluid. |
| Analysis | - Allows analysis of all faces of the component. - Visible expulsion of particles, ash, or other contaminants. |
- Reduced analysis and diagnostic capability. - No visibility of the expelled material causing obstruction. |
| Safety | - Uses air as the cleaning agent. - Localized cleaning of the entire component. - Does not use chemicals or abrasives. |
- Uses water as the primary cleaning agent. - Higher fracture risk, force concentrates on the central zone. |
| Obstruction Test | - Measured by air passage. | - When conducted, uses water passage, which has very different properties than vehicle exhaust gases. |
| Assembly | - Similar to an original new filter assembly. | - Requires assembly without probes to allow evaporating residues from cleaning. |
As mentioned earlier, the exhaust system is very complex and influences many other vehicle systems, such as the engine’s electronic management, fuel injection, exhaust gas recirculation, and turbocharger pressure. Changes to the exhaust system, such as removing the particle filter, will affect the functioning and performance of all other systems.
Besides being illegal, these changes greatly increase the emission levels of vehicles, especially cancerous solid particles. At a time when it is essential to protect the environment, these changes directly harm public health and should be condemned.