This article will briefly cover the differences between the safety systems found in vehicles and their classification, giving more relevance to active safety systems and ADAS systems. It will also explain the function of some systems found in current vehicles, as well as the main sensors and their features.
Current vehicles have increasingly developed and numerous driver assistance systems, with car manufacturers making significant investments in the development of safety systems in the vehicles they offer to the market.
Automobile safety systems can be divided into two main classes: active safety systems and passive safety systems.
Don’t hesitate! Your safety on the road is our priority. We are ready to assist you!
Below are some of the main systems we can find in current vehicles and their main functional objectives.
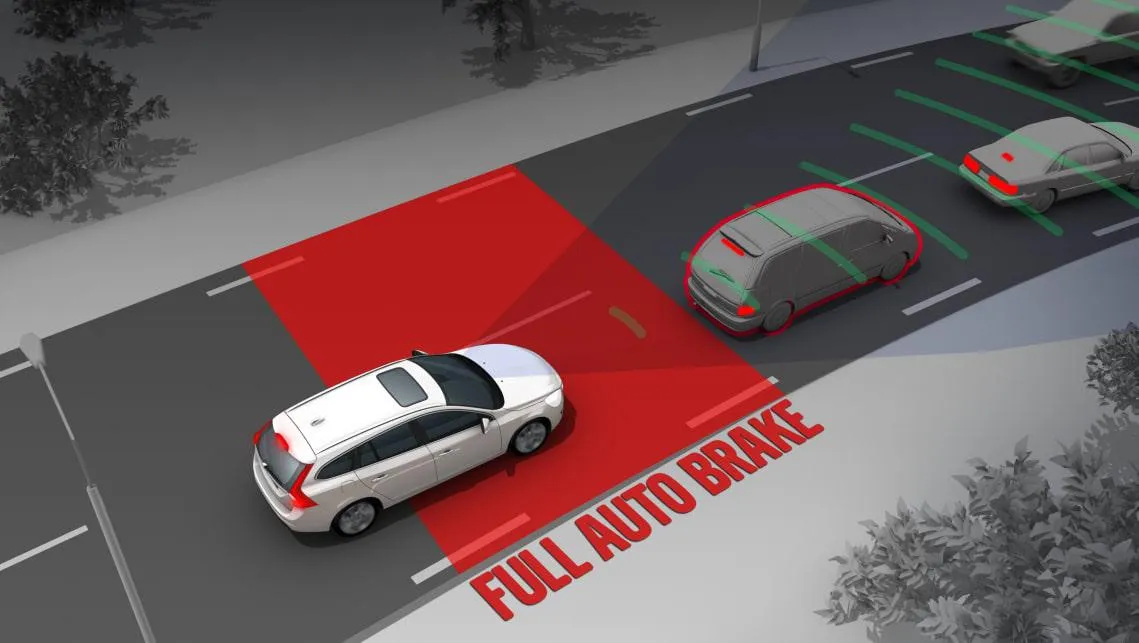
Figure 1 - AEB Systems
With the continuous development of safety systems, ADAS systems are becoming more and more advanced, contributing to vehicle automation and accident prevention. The sensors responsible for these systems are being improved to detect objects more precisely and in a greater range of conditions, ensuring greater safety for drivers and passengers.
The evolution of ADAS systems has brought immense changes to driving. It is increasingly common to see systems such as lane-keeping assistance, automatic braking, and others present in new vehicles, making driving safer and more comfortable.
If you would like more information about our services or have any questions, feel free to reach out to us. We are here to help!
To continuously improve these systems, it is necessary to have a more detailed map of the vehicle's surrounding space, as outlined in Figure 1. In addition to the coverage area and reading angle, the accuracy, robustness, and reliability of the systems are essential under various operating conditions.
ADAS systems use, in addition to the vehicle's standard sensors, three main types of additional sensors:
There are no perfect sensors for all situations that meet all the necessary requirements in any type of environment or scenario. To build a more capable global system, "Sensor Fusion" is performed, where the system uses information from multiple sensors for the same specific measurement. This takes advantage of each sensor type's strengths, resulting in more reliable information.
In Figure 4, a summary table is presented showing the strengths and weaknesses of each sensor type under different reading conditions and environments.
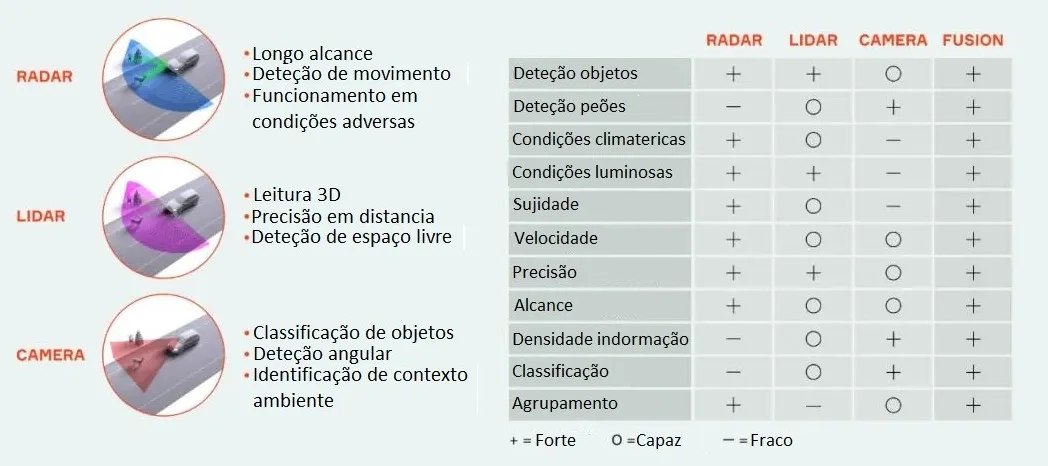
Figure 4 - Sensor Fusion - ADAS
ADAS systems have been on the market for several years and are becoming increasingly common, being found in vehicles of all segments. Starting in 2022, all new vehicles released in the European market will have ADAS systems.
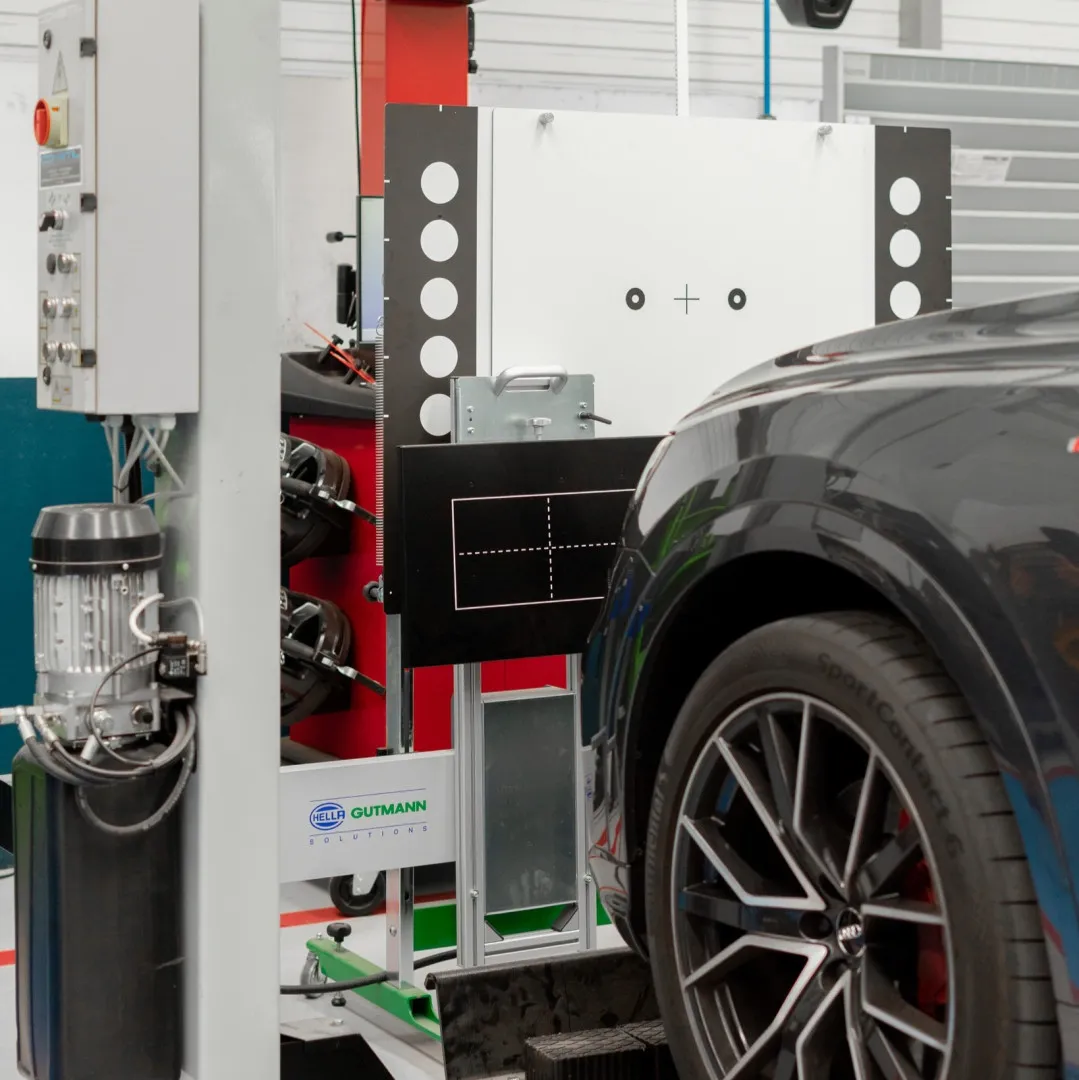
ADAS systems present another challenge for the aftermarket sector; some operations that were previously simple will now require the ADAS system to be calibrated to ensure correct functioning in all situations of these safety systems.
LD Auto recommends that ADAS calibrations be performed by technicians trained to carry out the operation with certified equipment to ensure that all manufacturer procedures and tolerances are respected.